Sleep is the foundation of our health, yet for those with complex sleep apnea, every night is a battle for breath. Unlike common snoring, this condition is a sophisticated challenge that affects both the body and brain. Understanding the nuances of this disorder is the first step toward reclaiming your energy and protecting your long-term health.
What is Complex Sleep Apnea?
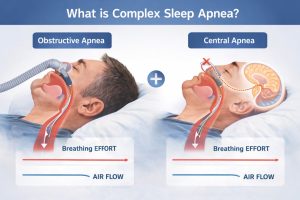
Complex sleep apnea (CompSAS), also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, is a unique hybrid of the different types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): A physical blockage of the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): A neurological issue where the brain fails to signal muscles to breathe.
It occurs in approximately 10-18% of patients initiating CPAP treatment for OSA.
In many cases, complex sleep apnea is identified when a patient begins treatment for OSA using a CPAP machine. While the machine clears the physical obstruction, the patient suddenly begins experiencing central apnea events, meaning their brain simply “forgets” to tell the body to take a breath.
What are the Symptoms and Treatments?
Because it involves both physical and neurological components, complex sleep apnea symptoms can be varied and intense. Recognizing these warning signs early is crucial for getting appropriate treatment.
Key Symptoms:
- Excessive Daytime Fatigue: Feeling exhausted despite a full night’s sleep.
- Morning Headaches: Often caused by oxygen deprivation and CO2 buildup.
- Frequent Nighttime Awakenings: Waking up gasping or choking.
- Cognitive Issues: Difficulty concentrating, brain fog, and memory lapses.
- Mood Changes: Increased irritability, anxiety, or depression.
Complex Sleep Apnea Treatment Options:
- Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV): Often the gold standard for CompSAS, this device monitors your breathing in real-time and adjusts pressure to maintain a steady rhythm.
- Bilevel PAP (BiPAP) with Backup Rate: This provides two different pressures and includes a “backup” to deliver a breath if you stop breathing for a set period.
- Lifestyle & Medication Review: Reducing opioid use or managing underlying heart conditions can often improve symptoms.
Is Complex Sleep Apnea Dangerous?
Yes. If left untreated, the strain on your system is significant. Is complex sleep apnea dangerous? Beyond the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, the repeated drops in blood oxygen (hypoxia) put your cardiovascular system under immense stress, increasing the risk of stroke, hypertension, and Type 2 diabetes.
Effect on Body and Brain Health
The sleep apnea effect on the brain and body health is profound. Chronic oxygen deprivation can lead to gray matter loss in the brain, impairing areas responsible for memory and emotional regulation. Over time, this neural damage and inflammation may even increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s or dementia.
Living with Complex Sleep Apnea: The Importance of Ongoing Management
Managing complex sleep apnea is not a one-time fix but rather an ongoing commitment to your health. Regular follow-up appointments with your sleep specialist are essential to monitor treatment effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. As your body adapts to therapy, pressure settings may need fine-tuning, or you might transition between different device types. Many patients report significant improvements in energy levels, mood, and cognitive function within weeks of starting proper treatment. Building a support network, whether through sleep apnea communities or working closely with your healthcare team, can make the journey more manageable and help you stay consistent with therapy.
Take the First Step: Test at Home
The path to better health starts with an accurate diagnosis. You no longer need to spend a night in a clinical lab to get answers. You can easily begin your journey with home sleep testing to determine the severity and type of your sleep apnea from the comfort of your own bed.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is complex sleep apnea different from regular sleep apnea?
Complex sleep apnea includes both airway blockage (obstructive) and brain-signal breathing pauses (central), often appearing during CPAP treatment for OSA.
Can complex sleep apnea go away on its own?
It usually needs treatment, but adjusting devices, medications, or treating underlying conditions can reduce or resolve symptoms under medical care.
What happens if it’s left untreated?
It can increase risks of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, diabetes, cognitive issues, and cause fatigue and poor quality of life.
Will I need a breathing machine forever?
Many need long-term therapy, but plans are personalized and may change with lifestyle or medical improvements and regular follow-ups.
Research-Based References
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM). (2025). New Guideline Provides Treatment Recommendations for Central Sleep Apnea.
- Morgenthaler, T. I., et al. (2006). Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Is It a Unique Clinical Syndrome? Sleep Medicine Reviews.
- Castronovo, V., et al. (2024). Severe Sleep Apnea Brain Damage is Reversible with CPAP. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.

Dr. Kunal Agarwal is a highly accomplished board-certified physician specializing in Family Medicine, Sleep Medicine, and Obesity Medicine. He completed his residency at Michigan State University and a fellowship at Henry Ford Health System, and has over a decade of experience delivering exceptional patient outcomes. Dr. Argarwal is passionate about patient education and advocacy, sleep disorders, and more. His expertise in treating sleep apnea is extremely valuable to improve his patients’ lives.
Awards, Honors, & Recognition
Top Doctor
SRQ Magazine and Sarasota Magazine, 2023-2024
Fellow of American Academy of Sleep Medicine (FAASM)
American Academy of Sleep Medicine, 2021
Named “Top Doctor” for 2017, 2018 (on cover), 2019,and 2020 by Delaware Today Magazine
2017-2020